Niantic Spatial Occlusion
Understanding Occlusion in Augmented Reality
If a virtual object appears in front of a real-world object that it should actually be behind, the AR illusion is broken. AR should seamlessly blend virtual objects into the real world and impart a sense of presence. Occlusion gives depth to virtual objects, allowing them to appear behind or in front of real-world objects. With proper occlusion, virtual content will appear to be physically present in the scene, blocking view of objects dynamically as the user moves their device through the space.
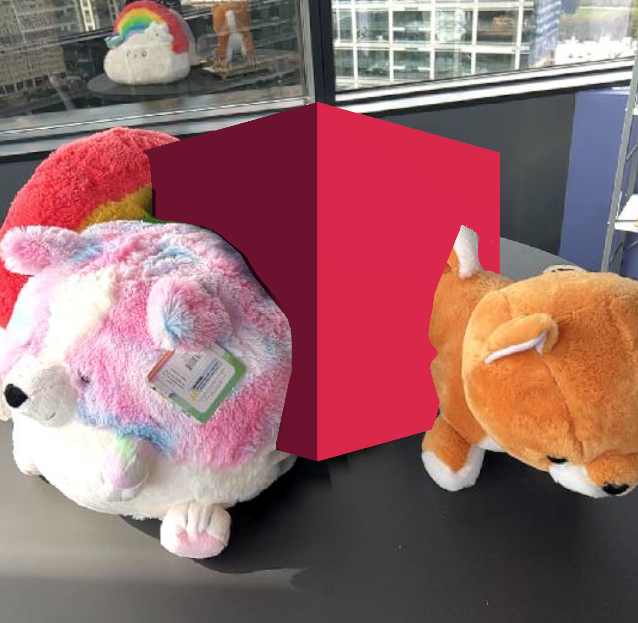
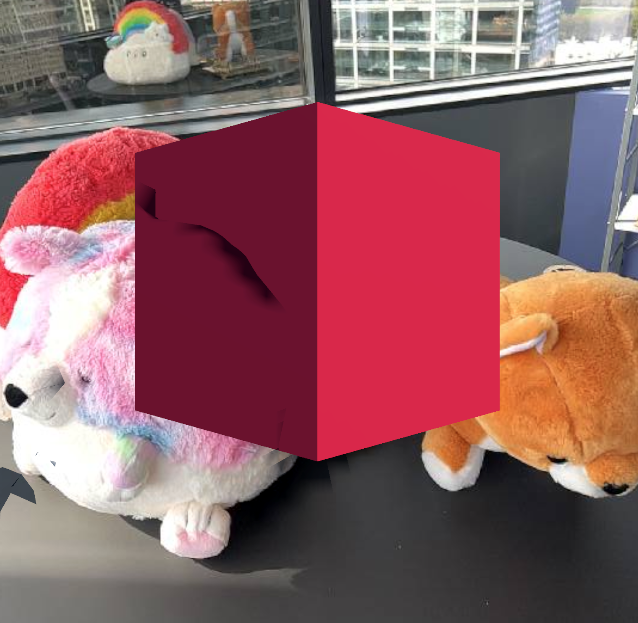

Left: AR without occlusion. Right: AR with real-world occlusion from NSDK.
Occlusion in NSDK
Occlusion is powered by depth sensing, and applications can choose which type of occlusion to use. Niantic Spatial SDK (NSDK) provides features that allow for swapping between dynamic and mesh-based occlusion depending on the needs of your application. This implementation works on any NSDK device or platform, regardless of lidar capability.
An example of occlusion as characters walk behind a tree
Types of Occlusion in NSDK
Instant Dynamic Occlusion (Fast, Noisy)
Dynamic occlusion directly refers to a depth buffer to perform occlusions. Depth buffers are either lidar frames or generated depth from NSDK using RGB camera frames. Since depth data is generated quickly, this type of occlusion is good at capturing fast-moving objects, like people or pets. However, just-in-time occlusion will not always line up with meshing and may over/under-occlude meshed objects.
Mesh Occlusion (Stable, Slow Occlusion)
Mesh-based occlusion uses a 3D mesh built from many depth frames and device poses by NSDK to determine occlusion surfaces. This technique averages a range of depth measurements, making it more accurate for static regions of the environment. This approach is more stable than instant dynamic occlusion and produces cleaner results, but updates are less frequent. Dynamic agents (like people and pets) may occlude less reliably.
Instant Depth + Mesh-Blended Occlusion (Unity SDK only)
Occlusion Stabilization has the advantages of both modes. It combines the fast response time of instant occlusion with the stable averaging effect of meshing. A depth map is produced from the NSDK mesh, rendered to a texture and combined with the latest depth buffer in a way that avoids flickering and Z-fighting.
More Information
For details on how to use this feature, see How to Setup Real-World Occlusion.